If you are a beginner and want to run Docker on your Windows machine, this guide will take you step by step from scratch. We’ll use Docker Desktop with WSL2 integration, which is the recommended and easiest way.
✅ Prerequisites
- Windows 10 (Build 19041 or later) or Windows 11
- Virtualization enabled in BIOS (Hyper-V or similar)
- Administrator privileges on your PC
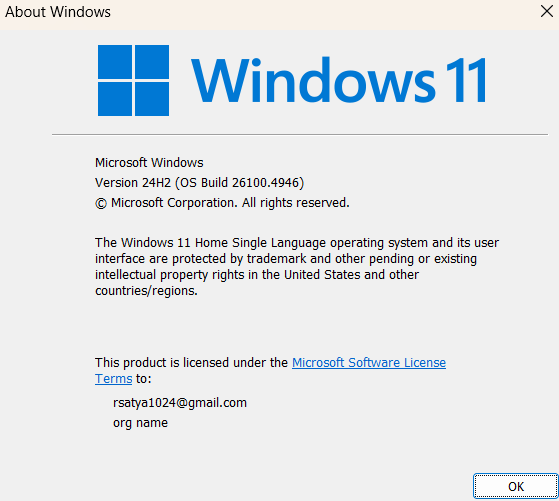
Step 1: Check your Windows version
Press Win + R, type ‘winver’, and press Enter.
Step 2: Install WSL2
🐧 What is WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux)?
Before we install Docker on Windows, it’s important to understand a key requirement: WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux).
🔹 WSL in Simple Words
WSL is a feature in Windows that allows you to run a Linux environment inside Windows — without setting up a virtual machine or dual-boot system.
Think of it as:
👉 “A Linux computer running inside your Windows machine.”
🔹 Why Do We Need WSL for Docker?
- Docker relies on Linux kernel features (like namespaces and cgroups).
- Since Windows doesn’t have these by default, WSL 2 provides a lightweight Linux kernel inside Windows.
- This makes it possible to run Linux containers on a Windows system smoothly.
🔹 WSL Versions
- WSL 1 – Older, slower, limited compatibility.
- WSL 2 – Latest version with a full Linux kernel and better performance. (✅ Recommended for Docker)
🔹 What Can You Do with WSL?
Once installed, you can open PowerShell or Windows Terminal and type:
wsl
And you’ll instantly drop into a Linux shell. From there, you can:
ls -l # List files
sudo apt update # Update Linux packages
sudo apt install python3 # Install Python
👉 In short:
WSL 2 is the backbone that allows Docker Desktop to run smoothly on Windows.
Without it, you cannot run Docker containers effectively.
Steps to install WSL
Open PowerShell as Administrator and run:
wsl –install
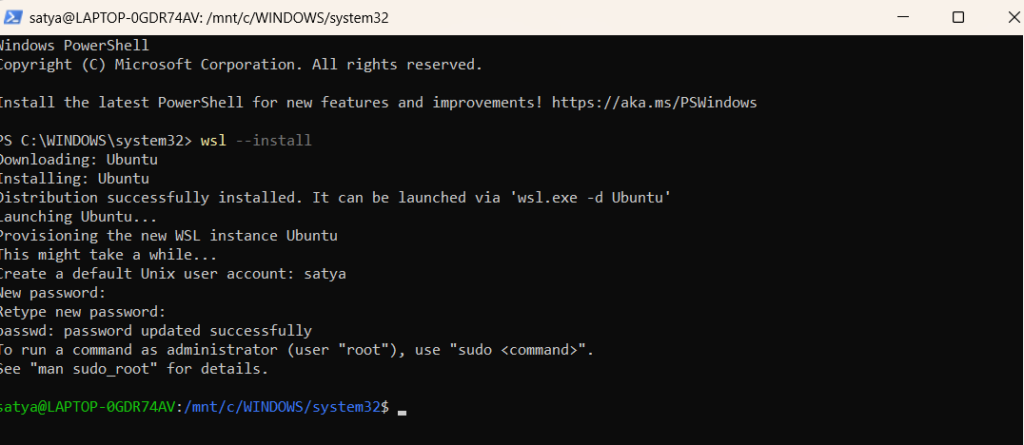
If you encounter any errors, then try restart and re install the wsl. vvvvvvvxIf you already have WSL, update it:
wsl –update
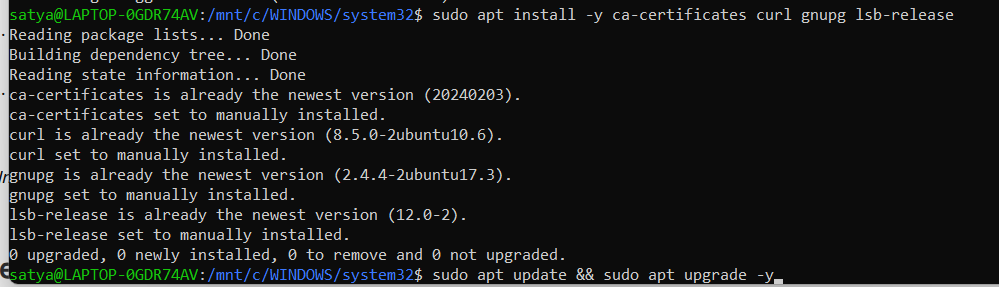
run the below two commands. these commands will updates and install all the required packages for Docker installation.
# sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
# sudo apt install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
Step 3: Download Docker Desktop
- Visit Docker Desktop Downloads.
- Download the installer for Windows (Docker Desktop Installer.exe).

Step 4: Install Docker Desktop
- Run Docker Desktop Installer.exe.
- Accept the license and follow the setup wizard.
- Allow the installer to configure WSL2 backend.
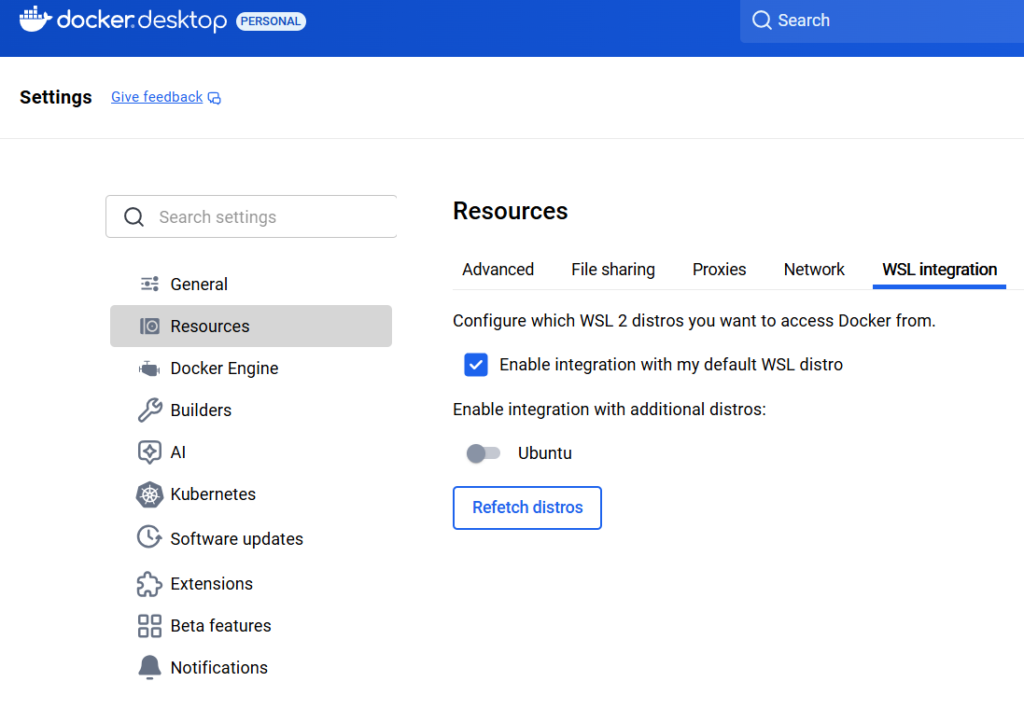
Step 5: Enable WSL Integration
- Open Docker Desktop → Settings → Resources → WSL Integration
- Enable your installed Linux distribution (e.g., Ubuntu).
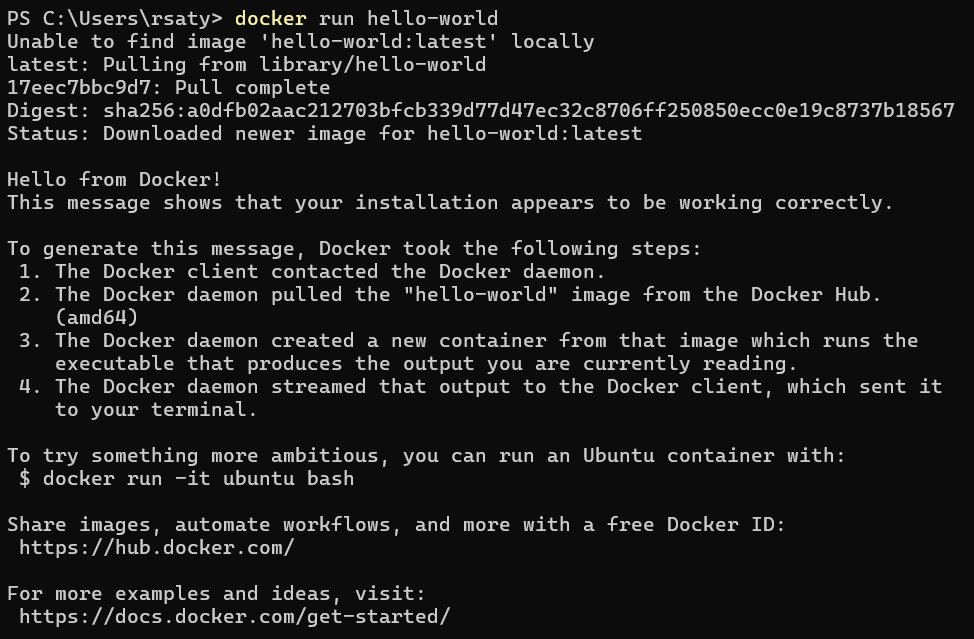
Step 6: Verify Installation
Open PowerShell or Command Prompt and run:
docker –version
docker run hello-world
If Docker is installed correctly, you’ll see:
- The Docker version number
- A welcome message from the hello-world container
Troubleshooting Tips
- WSL not found → Update Windows and ensure wsl feature is enabled.
- Docker won’t start → Check BIOS virtualization and WSL2 setup.
- Permission issues → Run PowerShell as Administrator.
<-Read Previous Article- -Read Next Article->
Also Read
The below rest of the articles give you the more information about the Docker and OAuth in PinFederate. You may love reading them.
(OIDC)Open ID Connect in ping federate,obtaining postman token and json web token
Components of OAuth 2.0 in PingFederate
Understanding OAuth Grants: Types, Flows, and Applications
Authorization Code Grant Flow in OAuth 2.0
OAuth Implicit Flow in PingFederate
Authorization Code with PKCE Flow | PingFederate
Client Credentials Grant Type in OAuth 2.0
Resource Owner Password Credentials (ROPC) Grant Flow in OAuth 2.0
Refresh Tokens in PingFederate OAuth 2.0
OAuth 2.0 Introspection Endpoint
PingFederate OAuth 2.0 UserInfo Endpoint
PingFederate OAuth 2.0 Token Revocation Endpoint
Exploring OpenID Connect (OIDC) in PingFederate
An Introduction to Identity and Access Management
Understanding the SAML Authentication Flow for IDP Initiated SSO
Understanding the SAML SP-Initiated Single Logout (SLO) Flow
LDAP Overview: Architecture, Terminologies, and Data Storage
PKCE WITH OAUTH 2.0 IN PING FEDERATE
Implicit Grant in PingFederate ,postman token and json web token
(ROPC)Resource owner password credentials in ping federate,postman and json web tokens